Byblos
« The Stela of the Viceroy Usersatet (Boston MFA 25.632), his Shrine at Qasr Ibrim, and the Festival of Nubian Tribute under Amenhotep II »
ENiM 7, 2014, p. 239-276.
 La stèle de Semna, du vice-roi de Nubie de la XVIIIe dynastie, Ousersatet, consigne un conseil donné par Amenhotep II à son vice-roi sous la forme d’une copie monumentale de la transcription personnelle du roi de son propre décret royal à Ousersatet. Le décret fut promulgué durant une fête célébrant l’accession royale, à une date secondaire, apparemment pour lier l’accession royale à la fête k?-?r-k?, à l’image de Ramsès III qui, plus tard, célébrera à la fois son accession et une fête de l’accession royale associée à la fête de Néhebkaou. Dans ce texte, Amenhotep II conseille Ousersatet quant aux interactions des Égyptiens et Nubiens avec l’administration du vice-roi et éclaire un peu les relations entre le roi, le vice-roi et les membres nubiens de la bureaucratie égyptienne du sud. La nature apparemment obscure et poétique du conseil royal et le manque de clarté quant à la situation d’Amenhotep II lorsqu’il le prodigue expliquent l’attention portée à ce texte, mais un certain manque de rigueur dans l’interprétation a obscurci plusieurs analyses de l’inscription. Un nouveau collationnement et un examen du texte de la stèle révèlent qu’Amenhotep II aborde apparemment la question de l’intégration croissante, par le vice-roi, de Nubiens dans les niveaux les plus élevés de l’administration du sud. Amenhotep II utilise une formule apparemment proverbiale qui fait référence à la transmission de l’autorité plus ancienne du vice-roi aux plus grandes divisions de la bureaucratie, et à la création d’un équivalent nubien du vice-roi, ce dernier restant néanmoins le primus inter pares de l’administration.
La stèle de Semna, du vice-roi de Nubie de la XVIIIe dynastie, Ousersatet, consigne un conseil donné par Amenhotep II à son vice-roi sous la forme d’une copie monumentale de la transcription personnelle du roi de son propre décret royal à Ousersatet. Le décret fut promulgué durant une fête célébrant l’accession royale, à une date secondaire, apparemment pour lier l’accession royale à la fête k?-?r-k?, à l’image de Ramsès III qui, plus tard, célébrera à la fois son accession et une fête de l’accession royale associée à la fête de Néhebkaou. Dans ce texte, Amenhotep II conseille Ousersatet quant aux interactions des Égyptiens et Nubiens avec l’administration du vice-roi et éclaire un peu les relations entre le roi, le vice-roi et les membres nubiens de la bureaucratie égyptienne du sud. La nature apparemment obscure et poétique du conseil royal et le manque de clarté quant à la situation d’Amenhotep II lorsqu’il le prodigue expliquent l’attention portée à ce texte, mais un certain manque de rigueur dans l’interprétation a obscurci plusieurs analyses de l’inscription. Un nouveau collationnement et un examen du texte de la stèle révèlent qu’Amenhotep II aborde apparemment la question de l’intégration croissante, par le vice-roi, de Nubiens dans les niveaux les plus élevés de l’administration du sud. Amenhotep II utilise une formule apparemment proverbiale qui fait référence à la transmission de l’autorité plus ancienne du vice-roi aux plus grandes divisions de la bureaucratie, et à la création d’un équivalent nubien du vice-roi, ce dernier restant néanmoins le primus inter pares de l’administration.
 The Semna stela of the Eighteenth Dynasty Viceroy of Nubia, Usersatet, records Amenhotep II’s advice to his viceroy in the form of a monumental copy of the king’s personal transcription of his own royal decree to Usersatet. The decree was issued during a festival celebrating the royal accession on a secondary date, apparently in order to link the king’s accession to the k?-?r-k? festival, just as Ramesses III later would celebrate both his actual accession and a festival of royal accession associated with the Nehebkau festival. Amenhotep II offers advice to Usersatet regarding interactions of Egyptians and Nubians within the viceregal administration, and shed some light on the interactions of king, viceroy, and Nubian members of the Egyptian bureaucracy in the south. The seemingly obscure and poetic nature of the king’s advice, and the lack of clarity regarding the situation about which Amenhotep II offers his advice, have led to considerable modern attention to the text, but a certain looseness of interpretation has plagued many examinations of the inscription. A new collation of the stela, and an examination of the text, reveal that Amenhotep II was apparently addressing the viceroy’s increasing integration of Nubians into the higher levels of the southern administration. Amenhotep II quotes an apparently proverbial saying that refers to a devolution of earlier viceregal authority into greater divisions of bureaucracy, and the creation of a Nubian counterpart to the viceroy, the latter remaining nevertheless the primus inter pares of the administration.
The Semna stela of the Eighteenth Dynasty Viceroy of Nubia, Usersatet, records Amenhotep II’s advice to his viceroy in the form of a monumental copy of the king’s personal transcription of his own royal decree to Usersatet. The decree was issued during a festival celebrating the royal accession on a secondary date, apparently in order to link the king’s accession to the k?-?r-k? festival, just as Ramesses III later would celebrate both his actual accession and a festival of royal accession associated with the Nehebkau festival. Amenhotep II offers advice to Usersatet regarding interactions of Egyptians and Nubians within the viceregal administration, and shed some light on the interactions of king, viceroy, and Nubian members of the Egyptian bureaucracy in the south. The seemingly obscure and poetic nature of the king’s advice, and the lack of clarity regarding the situation about which Amenhotep II offers his advice, have led to considerable modern attention to the text, but a certain looseness of interpretation has plagued many examinations of the inscription. A new collation of the stela, and an examination of the text, reveal that Amenhotep II was apparently addressing the viceroy’s increasing integration of Nubians into the higher levels of the southern administration. Amenhotep II quotes an apparently proverbial saying that refers to a devolution of earlier viceregal authority into greater divisions of bureaucracy, and the creation of a Nubian counterpart to the viceroy, the latter remaining nevertheless the primus inter pares of the administration.
 Consulter cet article (27203) -
Consulter cet article (27203) -  Télécharger cet article au format pdf (18256)
Télécharger cet article au format pdf (18256)
« EntitĂ©s divines et lieux de cultes Ă Byblos entre le IIe et le Ie millĂ©naire d’après les inscriptions hiĂ©roglyphiques giblites »
ENiM 16, 2008, p. 205-228.
 Cet article aborde la question de l’identification des divinités des temples de Jbeil/Byblos (Liban) à travers les sources hiéroglyphiques du IIe millénaire mises au jour dans les deux ensembles cultuels principaux de l’acropole : le temple de la Baalat Gebal, « la Dame de Byblos », divinité poliade ; et le temple aux Obélisques, un temple à vocation multiples. De nombreux chercheurs ont tenté de savoir qui se cachait derrière la Dame de Byblos mais cette recherche est peut-être vaine car la Baalat Gebal semble être une entité divine à part entière. Si son identification à Anat, Astarté ou encore Hathor est véridique, celle-ci a très bien pu changer au cours de la longue période d’attestation de la déesse. Ces questions sont explorées à la lumière des sources hiéroglyphiques. Quant au second ensemble cultuel, le temple aux Obélisques, il a été attribué anciennement à Reshef, mais cette attribution se fonde sur une lecture erronée du nom d’Hérichef sur un relief en hiéroglyphes. En outre, de nombreux autres théonymes égyptiens sont attestés sur ces mêmes documents : Nout, Rê-Horakhty, la Grande Ennéade et la Petite Ennéade. En s’aidant des textes phéniciens plus tardifs on peut comprendre ces théonymes comme une « interpretatio aegyptiaca » des dieux sémitiques par une population sémitique égyptianisée. On pourrait donc en réalité avoir à faire à Anat, Shamash, et « l’assemblée des dieux saints de Byblos » (KAI 4).
Cet article aborde la question de l’identification des divinités des temples de Jbeil/Byblos (Liban) à travers les sources hiéroglyphiques du IIe millénaire mises au jour dans les deux ensembles cultuels principaux de l’acropole : le temple de la Baalat Gebal, « la Dame de Byblos », divinité poliade ; et le temple aux Obélisques, un temple à vocation multiples. De nombreux chercheurs ont tenté de savoir qui se cachait derrière la Dame de Byblos mais cette recherche est peut-être vaine car la Baalat Gebal semble être une entité divine à part entière. Si son identification à Anat, Astarté ou encore Hathor est véridique, celle-ci a très bien pu changer au cours de la longue période d’attestation de la déesse. Ces questions sont explorées à la lumière des sources hiéroglyphiques. Quant au second ensemble cultuel, le temple aux Obélisques, il a été attribué anciennement à Reshef, mais cette attribution se fonde sur une lecture erronée du nom d’Hérichef sur un relief en hiéroglyphes. En outre, de nombreux autres théonymes égyptiens sont attestés sur ces mêmes documents : Nout, Rê-Horakhty, la Grande Ennéade et la Petite Ennéade. En s’aidant des textes phéniciens plus tardifs on peut comprendre ces théonymes comme une « interpretatio aegyptiaca » des dieux sémitiques par une population sémitique égyptianisée. On pourrait donc en réalité avoir à faire à Anat, Shamash, et « l’assemblée des dieux saints de Byblos » (KAI 4).
 This article explores the identification of deities in the temples of Jbeil/Byblos (Lebanon), using 2nd millennium BC hieroglyphic sources discovered in the two main religious complexes: the temple of Baalat Gebal, “the Lady of Byblos,” a poliad deity; and the temple of the Obelisks, a multifunctional temple. Many researchers have attempted to determine the identity of the Lady of Byblos. However, this quest may have been in vain, as Baalat Gebal appears to be a distinct divine entity in her own right. If her identification with Anat, Astarte, or Hathor is accurate, it might have evolved during the lengthy period of the goddess’s attestation. In this article we explore these questions in light of hieroglyphic sources. The Obelisk Temple was previously attributed to Reshef, but this connection was based on an erroneous reading of Herichef’s name on a hieroglyphic relief. Moreover, numerous other Egyptian theonyms are attested in these documents: Nut, Ra-Harakhty, the Great Ennead, and the Small Ennead. Drawing on later Phoenician texts, these theonyms can be interpreted as an “interpretatio aegyptiaca” of Semitic gods by an Egyptianized Semitic population. Hence, they might be referring to Anat, Shamash, and “the assembly of the holy gods of Byblos.”
This article explores the identification of deities in the temples of Jbeil/Byblos (Lebanon), using 2nd millennium BC hieroglyphic sources discovered in the two main religious complexes: the temple of Baalat Gebal, “the Lady of Byblos,” a poliad deity; and the temple of the Obelisks, a multifunctional temple. Many researchers have attempted to determine the identity of the Lady of Byblos. However, this quest may have been in vain, as Baalat Gebal appears to be a distinct divine entity in her own right. If her identification with Anat, Astarte, or Hathor is accurate, it might have evolved during the lengthy period of the goddess’s attestation. In this article we explore these questions in light of hieroglyphic sources. The Obelisk Temple was previously attributed to Reshef, but this connection was based on an erroneous reading of Herichef’s name on a hieroglyphic relief. Moreover, numerous other Egyptian theonyms are attested in these documents: Nut, Ra-Harakhty, the Great Ennead, and the Small Ennead. Drawing on later Phoenician texts, these theonyms can be interpreted as an “interpretatio aegyptiaca” of Semitic gods by an Egyptianized Semitic population. Hence, they might be referring to Anat, Shamash, and “the assembly of the holy gods of Byblos.”
 Consulter cet article (6759) -
Consulter cet article (6759) -  Télécharger cet article au format pdf (4402)
Télécharger cet article au format pdf (4402)
ENiM 15 - 2022
16 article(s) - 25 juillet 2024.
ENiM 1 à 17 (2008-2024) : 217 articles
3 183 171 téléchargements
5 057 253 consulations.
Index des auteurs
Mots clés
Derniers articles : 
TDENiM - Mise en ligne des volumes Ă©puisĂ©s : 
CENiM - Mise en ligne des volumes Ă©puisĂ©s : 
 Jean-Claude Grenier L'Osiris ANTINOOS, CENiM 1, Montpellier, 2008 — (26 dĂ©cembre 2008)
Jean-Claude Grenier L'Osiris ANTINOOS, CENiM 1, Montpellier, 2008 — (26 dĂ©cembre 2008) 
 Twitter
Twitter 

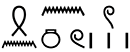 , šnnw.w / šnn.w, « manoeuvres dormantes »
, šnnw.w / šnn.w, « manoeuvres dormantes »






 Contact
Contact